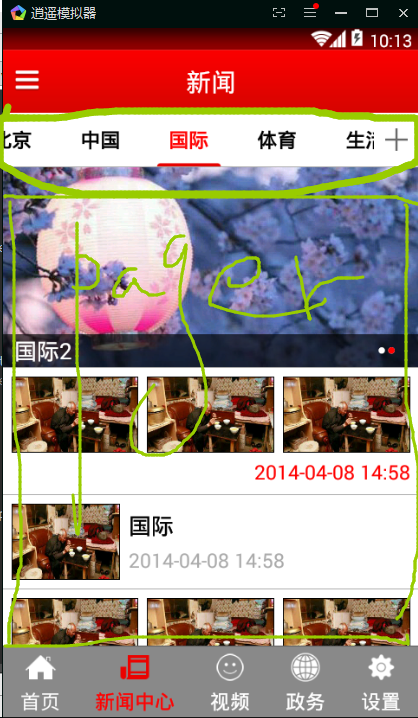
TabPagerIndicator使用
本文共 1433 字,大约阅读时间需要 4 分钟。
 1 注意/在清单文件中配置activity/theme=
1 注意/在清单文件中配置activity/theme=
android:theme="@style/Theme.PageIndicatorDefaults">
// 2 (adpter中添加getPageTitle)
2 (adpter中添加getPageTitle)
//1.给viewPager设置数据适配器 MyPagerAdapter myPagerAdapter = new MyPagerAdapter(); pager.setAdapter(myPagerAdapter); //2.指示器和viewPager进行绑定 indicator.setViewPager(pager);
3 重点(修改选中文字的颜色,背景) values/style/tabPageIndicator
values/style/tabPageIndicator
@android:color/transparent 为加背景,,不能用@null
<item name="vpiTabPageIndicatorStyle">@style/Widget.TabPageIndicator</item>//这里
</style>
<style name="Widget"> </style> <style name="Widget.TabPageIndicator" parent="Widget"> <item name="android:gravity">center</item><item name="android:background">@drawable/vpi__tab_indicator</item>//背景
<item name="android:paddingLeft">22dip</item> <item name="android:paddingRight">22dip</item> <item name="android:paddingTop">12dp</item> <item name="android:paddingBottom">12dp</item> <item name="android:textAppearance">@style/TextAppearance.TabPageIndicator</item> <item name="android:textSize">12sp</item> <item name="android:maxLines">1</item> </style> <style name="TextAppearance.TabPageIndicator" parent="Widget"> <item name="android:textStyle">bold</item><item name="android:textColor">@color/vpi__dark_theme</item>//文字颜色
</style> <style name="Widget.IconPageIndicator" parent="Widget"> <item name="android:layout_marginLeft">6dp</item> <item name="android:layout_marginRight">6dp</item> </style></resources>
你可能感兴趣的文章
MySQL的10种常用数据类型
查看>>
MySQL的btree索引和hash索引的区别
查看>>
mysql的cast函数
查看>>
MySql的CRUD(增、删、改、查)操作
查看>>
MySQL的DATE_FORMAT()函数将Date转为字符串
查看>>
mysql的decimal与Java的BigDecimal用法
查看>>
MySql的Delete、Truncate、Drop分析
查看>>
MySQL的Geometry数据处理之WKB方案
查看>>
MySQL的Geometry数据处理之WKT方案
查看>>
mysql的grant用法
查看>>
Mysql的InnoDB引擎的表锁与行锁
查看>>
mysql的InnoDB引擎索引为什么使用B+Tree
查看>>
MySQL的InnoDB默认隔离级别为 Repeatable read(可重复读)为啥能解决幻读问题?
查看>>
MySQL的insert-on-duplicate语句详解
查看>>
mysql的logrotate脚本
查看>>
MySQL的my.cnf文件(解决5.7.18下没有my-default.cnf)
查看>>
MySQL的on duplicate key update 的使用
查看>>
MySQL的Replace用法详解
查看>>
mysql的root用户无法建库的问题
查看>>
mysql的sql_mode参数
查看>>